Abel’s security features give you control over access to screens and data in Abel. A good access strategy can also enhance productivity and user experience by giving each user only the functions they need.
In this blog we’ll touch on these areas:
- Functional Security settings define the functions and screens a user can access, and what actions they’re allowed
- Data Visibility settings define the sub-sets of data each user normally works to improve productivity and usability
- Multi Database credentials for seamless access between Abel databases
These features combine to give each user access to the functions and data they need to do their work.
Functional Security
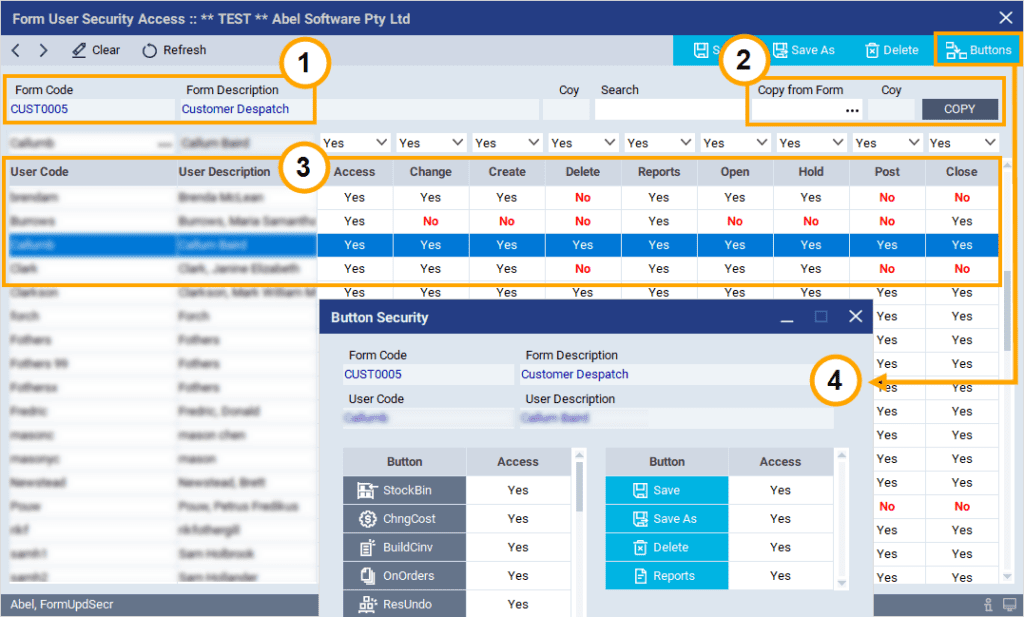
With Abel’s Functional Security, you can define Access, Change, Create, Delete and Print permissions for users and screens. Also, for documents such as customer orders and invoices you can specify which users are allowed to Open, Hold, Post or Close them.
You can maintain security from a User perspective or from a Screen perspective like this example:
- The header identifies the screen that the security settings are for
- You can copy the security profile from another screen if required
- The table defines the permitted actions for each user or role
- The popup defines button security for a selected user or role
Data Visibility
The Data Visibility settings are optional. They define the data a user normally works with. These settings improve usability in larger businesses by presenting the most relevant data for each user. Here are some examples:
- Define which companies or branches in your organization that each user works with
- Filter which group of clients a particular account manager works with
- Filter a user’s data by employee, team, region or a combination of these
Multi-Database Credentials
For multi-database implementations of Abel, users have matching credentials in each of the databases that they are permitted to access. This enables them to navigate seamlessly between databases. For more on Abel’s inter-database features, including inter-database navigation, refer to our Enterprise Management section.
